อนาคตการใช้ Generative AI ในภาคองค์กร
โดย ไบรอัน เบิร์ก รองประธานฝ่ายวิจัยด้านนวัตกรรมและเทคโนโลยี การ์ทเนอร์ อิงค์
แม้ ChatGPT จะมีความสามารถที่น่าสนใจแต่ก็เรียกได้ว่ายังอยู่ในขั้นเริ่มต้น ซึ่งการใช้งาน Generative AI ในภาคองค์กรนั้นไปไกลและซับซ้อนกว่ามาก
ช่วงสามปีที่ผ่านมา มีบริษัท Venture Capital (VC) หลายแห่งลงทุนในโซลูชัน Generative AI ต่าง ๆ เป็นมูลค่ามากกว่า 1.7 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐฯ โดยเฉพาะการลงทุนกับการค้นพบยาด้วย AI และการเข้ารหัสซอฟต์แวร์ AI เป็นสองกลุ่มที่ได้รับเงินทุนมากที่สุด
โมเดลพื้นฐานในยุคแรก ๆ เช่น ChatGPT โฟกัสไปยังความสามารถของ Generative AI เพื่อเสริมงานด้านครีเอทีฟ แต่เราคาดว่าภายในปี ค.ศ. 2025 ยาและวัสดุการผลิตใหม่ ๆ มากกว่า 30% จะเป็นการค้นพบอย่างเป็นระบบโดยการใช้เทคนิค Generative AI จากที่วันนี้ไม่มีเลย นั่นเป็นเพียงหนึ่งในตัวอย่างของ Use Case มากมายของการนำ Generative AI มาใช้ในอุตสาหกรรม
Use Case ต่าง ๆ ของการใช้ Generative AI
Generative AI สามารถใช้สำรวจความเป็นไปได้ของการออกแบบวัตถุได้หลากหลายเพื่อค้นหาสิ่งที่เหมาะสมที่สุด ไม่เพียงแต่เสริมและเร่งการออกแบบในหลาย ๆ ด้านเท่านั้น แต่ยังมีศักยภาพในการ “ประดิษฐ์คิดค้น (Invent)” นวัตกรรมการออกแบบ หรือ วัสดุที่มนุษย์อาจมองพลาดไปเป็นอย่างอื่น
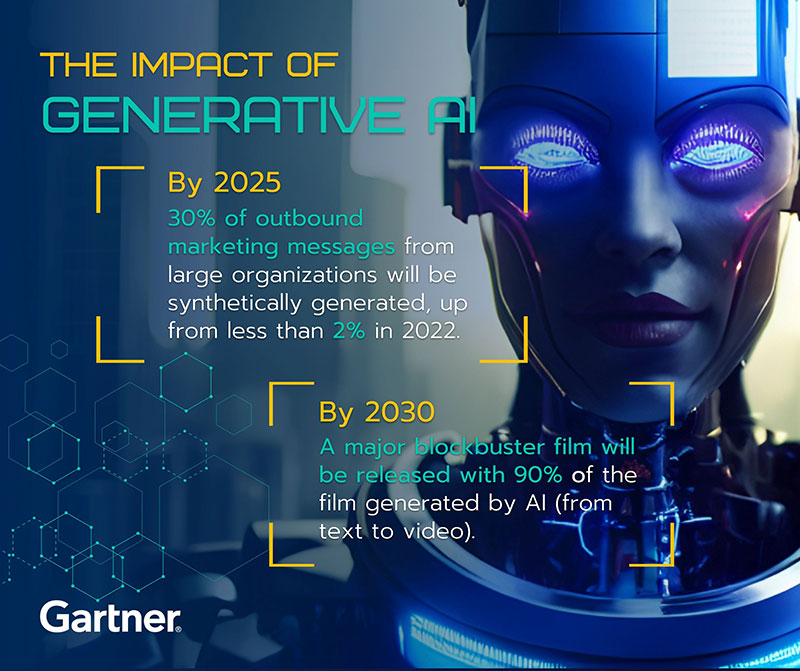
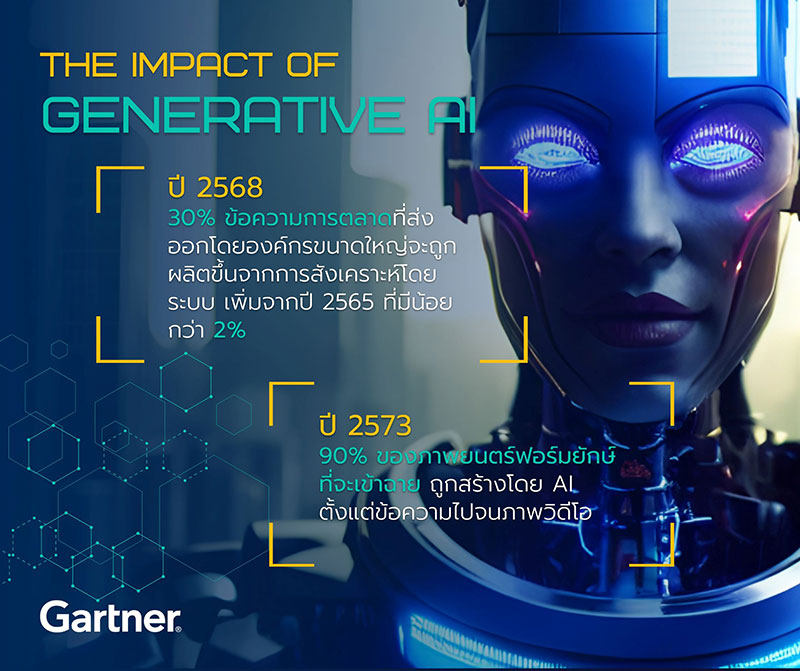
ในแวดวงการตลาดและสื่อต่างรับรู้ถึงผลกระทบของ Generative AI ซึ่งการ์ทเนอร์คาดว่า ภายในปี 2568 ประมาณ 30% ของข้อความด้านการตลาดที่ส่งออกโดยองค์กรใหญ่ ๆ จะถูกสร้างขึ้นจากการสังเคราะห์โดยระบบ โดยเพิ่มขึ้นจากปี 2565 ที่มีน้อยกว่า 2% นอกจากนี้ ภายในปี 2573 ประมาณ 90% ของภาพยนตร์ฟอร์มยักษ์ที่จะเข้าฉายจะสร้างด้วย AI (ตั้งแต่ตัวหนังสือไปจนภาพเคลื่อนไหว)
อย่างไรก็ตามโดยทั่วไปแล้วนวัตกรรมเอไอมักจะเกิดขึ้นอย่างรวดเร็ว ซึ่ง Generative AI ได้สร้าง Use Cases มากมายในอุตสาหกรรมต่าง ๆ
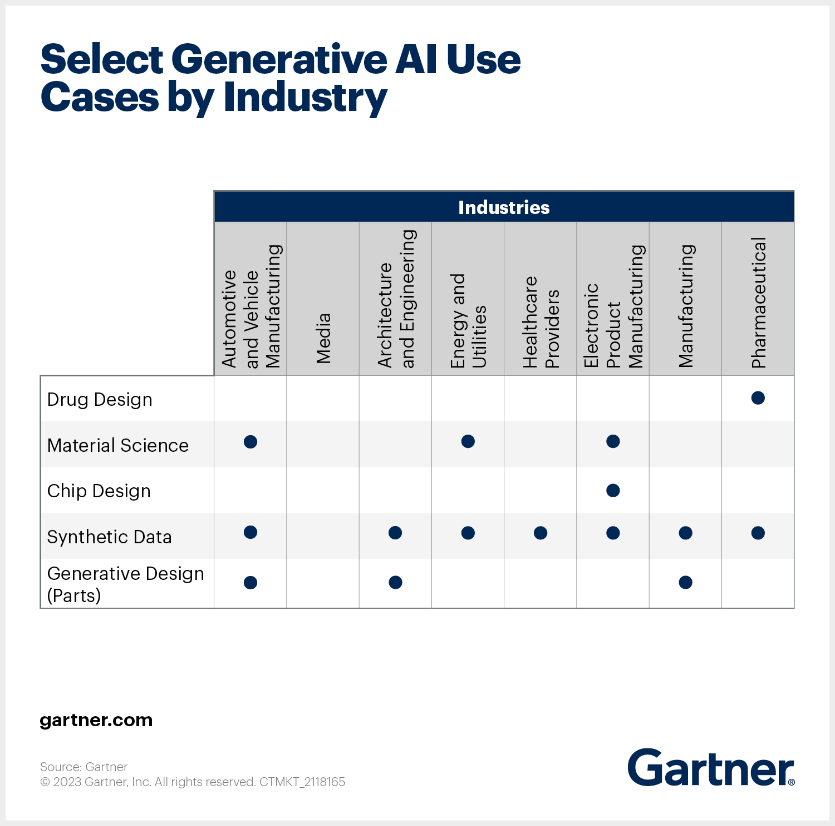
- การออกแบบและพัฒนายารักษาโรค (Drug Design)
Generative AI ถูกนำมาใช้ออกแบบและพัฒนายารักษาโรคสำหรับใช้ในกรณีต่าง ๆ แทนที่ต้องใช้เวลาหลายปี กลับย่นระยะเวลาให้เหลือเพียงไม่กี่เดือน เป็นโอกาสสำคัญของภาคเภสัชกรรมที่สามารถช่วยลดค่าใช้จ่ายและระยะเวลาในการค้นพบยาตัวใหม่ได้อย่างมีนัยสำคัญ
- วัสดุศาสตร์(Material Science)
เทคโนโลยี Generative AI กำลังส่งผลกระทบต่ออุตสาหกรรมยานยนต์ การบินและอวกาศ การป้องกันประเทศ การแพทย์ รวมถึงอุตสาหกรรมอิเล็กทรอนิกส์และพลังงาน โดยสามารถประกอบวัสดุขึ้นใหม่ทั้งหมดพร้อมกำหนดคุณสมบัติทางกายภาพได้อย่างเฉพาะ
กระบวนการนี้เรียกว่า Inverse Design สามารถกำหนดคุณสมบัติที่ต้องการและค้นหาวัสดุที่มีคุณสมบัติตรงตามที่กำหนดไว้ แทนที่จะอาศัยความบังเอิญเพื่อค้นหาวัสดุที่มีคุณสมบัติดังกล่าว ผลลัพธ์ที่ได้คือการค้นหา ตัวอย่างเช่น การค้นหาวัสดุที่เป็นตัวเหนี่ยวนำไฟฟ้าหรือมีแรงดึงดูดของแม่เหล็กมากกว่าวัสดุที่ใช้ในด้านพลังงานและการขนส่งในปัจจุบัน หรือการค้นหาวัสดุที่จำเป็นต้องมีความทนทานต่อการกัดกร่อน เป็นต้น
- การออกแบบชิป (Chip Design)
Generative AI สามารถใช้การเรียนรู้แบบเสริมกำลัง (Reinforcement Learning) ซึ่งเป็นเทคนิคหนึ่งทางด้าน Machine Learning สำหรับเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการจัดวางองค์ประกอบในการออกแบบแผงวงจรของเซมิคอนดักเตอร์ (Floorplanning) ซึ่ง Generative AI ช่วยย่นระยะเวลาของวงจรการพัฒนาผลิตภัณฑ์จากเดิมหลายสัปดาห์ที่ต้องทำงานร่วมกับผู้เชี่ยวชาญมนุษย์เหลือเป็นรายชั่วโมงแทน
- ข้อมูลสังเคราะห์ (Synthetic Data)
Generative AI เป็นหนทางเดียวในการสร้างข้อมูลสังเคราะห์ (Synthetic Data) ซึ่งเป็นประเภทข้อมูลที่ถูกสร้างขึ้นโดยอัลกอริทึมที่สำคัญกว่าข้อมูลที่รวบรวมโดยตรงมาจากบุคคลจริง ทำให้มั่นใจถึงความเป็นส่วนตัวของแหล่งข้อมูลดั้งเดิมที่ใช้ในการฝึกโมเดล ตัวอย่างเช่น ฐานข้อมูลด้านสุขภาพที่สามารถสร้างขึ้นเพื่อการวิจัยและวิเคราะห์โดยไม่ต้องเปิดเผยตัวตนของผู้ป่วย ซึ่งใช้เวชระเบียนรับรองความเป็นส่วนตัว
- การออกแบบชิ้นส่วนประกอบต่าง ๆ (Parts Design)
Generative AI ช่วยให้อุตสาหกรรมต่าง ๆ ประกอบด้วย ภาคการผลิต ยานยนต์ การบินและอวกาศ และการป้องกันประเทศ สามารถออกแบบชิ้นส่วนประกอบต่าง ๆ ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ เพื่อบรรลุเป้าหมายและข้อจำกัดได้ตามที่กำหนด อาทิ ในด้านประสิทธิภาพ ชนิดวัสดุและวิธีการผลิต ตัวอย่าง ผู้ผลิตรถยนต์สามารถใช้ Generative Design เพื่อคิดค้นการออกแบบที่เน้นน้ำหนักเบาขึ้น นำไปสู่เป้าหมายในการทำให้รถยนต์ประหยัดน้ำมันมากขึ้น เป็นต้น
การฝังเทคโนโลยีต่าง ๆ อย่างเหมาะสม
ปัจจุบันระบบ AI ส่วนใหญ่จะถูกแยกเป็นประเภทต่าง ๆ หมายความว่า มันสามารถรับการฝึกและแยกแยะความแตกต่างระหว่างภาพสุนัขและแมวได้ ซึ่ง Generative AI สามารถฝึกฝนให้สร้างภาพสุนัขหรือแมวที่ไม่มีอยู่ในโลกจริงได้ ซึ่งความสามารถในการสร้างสรรค์เทคโนโลยีนี้คือ Game Changer
Generative AI ทำให้ระบบต่าง ๆ สามารถสร้างสิ่งประดิษฐ์ที่มีมูลค่าสูงได้ อาทิ วิดีโอ การเล่าเรื่อง ข้อมูลการฝึกอบรม หรือแม้แต่การออกแบบและสร้างแผนผังวงจรไฟฟ้าหรืออิเล็กทรอนิกส์ต่าง ๆ
ตัวอย่างเช่น Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) ซึ่งเป็นเทคโนโลยีภาษาธรรมชาติขนาดใหญ่ ที่ใช้ในการเรียนรู้เชิงลึกเพื่อสร้างข้อความได้เหมือนมนุษย์ โดยในเจเนอเรชั่นที่ 3 (GPT-3) สามารถคาดการณ์คำที่จะใช้ในประโยคถัดไปตามการฝึกฝนที่สั่งสมมาในระบบ นอกจากนี้ยังสามารถเขียนเรื่องราว แต่งเพลงและประพันธ์บทกวี หรือแม้แต่เขียนโค้ดโปรแกรมในคอมพิวเตอร์ และ ChatGPT ยังช่วยนักเรียนทำการบ้านได้ในไม่กี่วินาที
นอกเหนือจากข้อความ (Text) แล้วยังสามารถสร้างภาพดิจิทัล อย่าง DALL·E 2, Stable Diffusion และ Midjourney ที่เป็น AI ที่สามารถสร้างภาพต่าง ๆ ได้จากข้อความ
ห้ามลืมเรื่องความเสี่ยง
ก่อนที่องค์กรจะเดินหน้าอย่างเต็มรูปแบบกับ Generative AI ต้องระลึกเสมอว่า นอกจากโอกาสทางธุรกิจแล้ว Generative AI ยังมีภัยคุกคามอยู่เช่นกัน เช่น ความเป็นไปได้ในการปลอมแปลงข้อมูลแบบ Deepfakes ปัญหาเรื่องลิขสิทธิ์ และการใช้เทคโนโลยี Generative AI ในทางที่ผิดเพื่อมุ่งเป้าโจมตีองค์กร
องค์กรต้องทำงานร่วมกับผู้บริหารด้านความปลอดภัยและจัดการความเสี่ยง เพื่อลดความเสี่ยงแบบเชิงรุกจากการเสื่อมเสียชื่อเสียง การปลอมแปลง การล่อลวง และในเรื่องของการเมือง ที่เกิดจากการใช้ Generative AI ในทางที่ผิดทั้งต่อปัจเจกบุคคล องค์กรธุรกิจและภาครัฐบาล
องค์กรควรพิจารณาคำแนะนำการใช้ Generative AI อย่างมีความรับผิดชอบ ผ่านรายชื่อผู้จัดจำหน่ายและผู้ให้บริการที่ได้รับการรับรอง พร้อมให้ความสำคัญกับองค์กรที่มีความมุ่งมั่นสร้างความโปร่งใสในชุดข้อมูลการฝึกอบรมและการใช้โมเดลอย่างเหมาะสม และ/หรือนำเสนอโมเดลของพวกเขาในโอเพ่นซอร์ส