การ์ทเนอร์เปิด 6 เทรนด์ช่วยผลักดันการนำเทคโนโลยี Metaverse มาใช้ในปัจจุบัน และจะยังเป็นเทรนด์หลักที่ขับเคลื่อนการใช้งานต่อไปอีก 3-5 ปีข้างหน้าอย่างต่อเนื่อง
มาร์ตี้ เรสนิค รองประธานฝ่ายวิจัยของการ์ทเนอร์ กล่าวในงาน Gartner IT Symposium/Xpo ระบุว่า “แม้การนำเทคโนโลยี Metaverse มาใช้จนเป็นที่แพร่หลายในตลาดนั้นจะกินเวลานานกว่า 10 ปี แต่ยังมีแนวทางปฏิบัติที่องค์กรสามารถนำไปใช้ได้ในขณะนี้ อาทิ ใช้ในโปรแกรมการอบรมและพัฒนาพนักงานใหม่ เพิ่มความสามารถทางการขาย ใช้เพื่อการศึกษาระดับสูง หรือจัดอบรมทักษะทางการแพทย์และการทหาร รวมถึงสร้างประสบการณ์ช็อปปิ้งเสมือนจริง”
“วันนี้ Metaverse ยังอยู่ในขั้นเริ่มต้น ทว่าแนวโน้มเทคโนโลยี กรณีการใช้งานที่ได้รับการยอมรับและผลลัพธ์ทางธุรกิจต่าง ๆ ที่เกิดจาก Metaverse กำลังเริ่มนำคุณค่าด้านนวัตกรรมเทคโนโลยีมาสู่องค์กร ซึ่ง Metaverse คือหนึ่งในเทคโนโลยีที่จะดิสรัปอุตสาหกรรมภาพรวม ถ้าองค์กรลงทุนระยะยาวและสร้างความแตกต่างได้อย่างแท้จริง” เรสนิคกล่าวเพิ่มเติม
การ์ทเนอร์ให้คำจำกัดความ Metaverse ว่าเป็น “การมีปฏิสัมพันธ์ที่เหนือขึ้นไปอีกขั้นระหว่างโลกเสมือนและโลกความจริง” โดยเทคโนโลยี Metaverse ทำให้ผู้คนสามารถมีตัวตนเสมือนหรือเสริมกิจกรรมทางกายภาพได้ ด้วยการส่งต่อหรือเพิ่มกิจกรรมทางกายภาพไปยังโลกเสมือน หรือในทางกลับกันจากกิจกรรมในโลกเสมือนจริงไปยังเป็นกิจกรรมจริง ๆ
การนำเทคโนโลยีต่าง ๆ ของ Metaverse มาใช้นั้นยังถือเป็นเรื่องใหม่และกระจัดกระจาย และการ์ทเนอร์ขอย้ำเตือนองค์กรให้ระมัดระวังการลงทุนสูง ๆ ในตลาด Metaverse เฉพาะว่า มันยังเร็วเกินไปที่จะทราบว่าควรลงทุนแบบใดเพื่อสร้างความสำเร็จในระยะยาว รวมถึงความเสี่ยงด้านจริยธรรม การเงิน และชื่อเสียงองค์กรในการลงทุนระยะแรก ๆ ที่ยังไม่ทราบความแน่ชัดของตลาด
“ใช้เวลานี้เรียนรู้ สำรวจ และเตรียมพร้อมรับมือโลก Metaverse ด้วยการจำกัดการนำมาใช้งาน และลองพิจารณา 6 เทรนด์นี้ที่อาจสร้างโอกาสใหม่ ๆ ให้แก่องค์กร” เรสนิค กล่าว
1.เกม (Gaming)
อุตสาหกรรมเกมโดยเฉพาะ “วิดีโอเกม” คือผู้ริเริ่มประสบการณ์และเทคโนโลยี Metaverse มาแล้วหลายปี ซึ่ง Metaverse จะใช้เทคโนโลยีการเล่นเกม วิธีการ เครื่องมือพัฒนาต่าง ๆ หรือแม้กระทั่งทฤษฎีของเกมมาสร้างประสบการณ์ทั้งในด้านการจำลองความบันเทิงและการอบรม โดยองค์กรธุรกิจจะนำ “Serious Games” หรือเกมที่ได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อวัตถุประสงค์มากกว่าแค่ความบันเทิง มาใช้เป็นเทคโนโลยีการเล่นเกม สร้างประสบการณ์ใหม่ ๆ และการเล่าเรื่องราวเพื่ออบรม รวมถึงจำลองภาระงานหรือฟังก์ชั่นทำงานที่มีความเฉพาะ
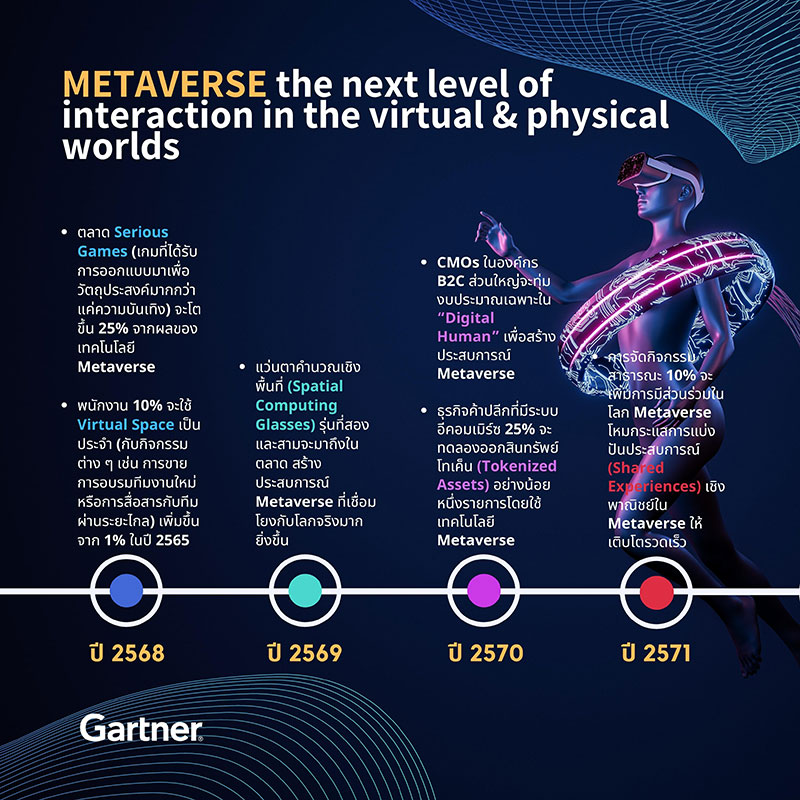
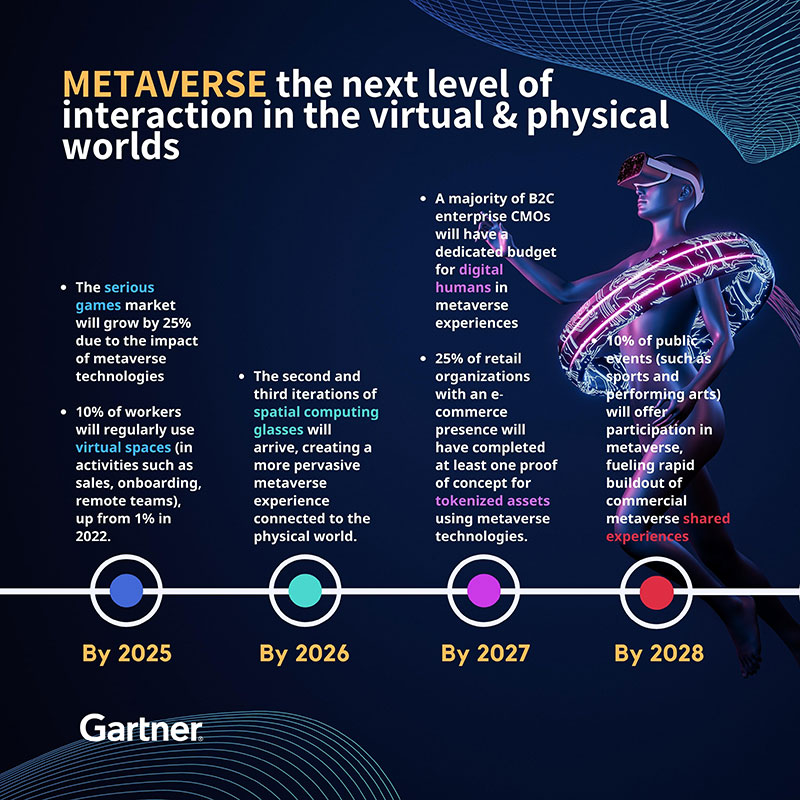
การ์ทเนอร์คาดการณ์ว่า ภายในปี พ.ศ. 2568 ตลาด Serious Games จะเติบโตเพิ่มขึ้น 25% จากผลกระทบเทคโนโลยี Metaverse
- มนุษย์ดิจิทัล (Digital Humans)
มนุษย์ดิจิทัล หรือ Digital Humans เป็นรูปแบบการสื่อสารโต้ตอบที่ขับเคลื่อนด้วย AI ซึ่งมีบุคลิกลักษณะ องค์ความรู้ และความคิดความอ่านแบบเดียวกับของมนุษย์ ปกติแล้วมักแสดงผลในรูปแบบของฝาแฝดดิจิทัล (Digital Twin) อวตารดิจิทัล (Avatar Digital) หุ่นยนต์ฮิวแมนนอยด์ (Humanoid Robots) หรือผ่านหน้าอินเทอร์เฟซการสนทนาของผู้ใช้ ซึ่งสามารถตีความคำพูด ท่าทางและรูปภาพ รวมถึงออกแบบคำพูด ปรับโทนเสียง และภาษากายของตนได้
องค์กรธุรกิจกำลังวางแผนใช้มนุษย์ดิจิทัลทำหน้าที่เป็นตัวแทนดิจิทัลภายในสภาพแวดล้อม Metaverse สำหรับงานบริการลูกค้า งานสนับสนุน งานขาย และการสร้างปฏิสัมพันธ์ร่วมกับกลุ่มลูกค้าปัจจุบันและลูกค้ากลุ่มเป้าหมาย การ์ทเนอร์คาดการณ์ว่า ภายในปี พ.ศ. 2570 ผู้บริหารซีเอ็มโอในองค์กร B2C ส่วนใหญ่จะทุ่มงบประมาณเฉพาะสำหรับ “Digital Humans” เพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์ Metaverse
- พื้นที่เสมือนจริง (Virtual Spaces)
พื้นที่เสมือนจริง หรือ โลกเสมือนจริง นั้นคือสภาพแวดล้อมที่สร้างขึ้นด้วยระบบคอมพิวเตอร์ เป็นพื้นที่ที่เปิดให้กลุ่มคนต่าง ๆ มาใช้ชีวิตออนไลน์ร่วมกันผ่านร่างอวตารหรือโฮโลแกรมส่วนบุคคล โดย Virtual Space นี้จะเปิดให้ผู้คนได้มีส่วนร่วมผ่านความรู้สึกหลากหลาย รับประสบการณ์เสมือนจริงและสร้างปฏิสัมพันธ์กันในพื้นที่ได้ อาทิ ใช้เพื่อเพิ่มโอกาสในการเข้าถึงกลุ่มลูกค้าที่ไม่สามารถหรือไม่สะดวกนัดหมายเจอหน้ากันตัวต่อตัว ใช้เป็นทางเลือกใหม่ในการเดินทาง หรือใช้เป็นพื้นที่ทำงานร่วมกันของพนักงาน
การ์ทเนอร์คาดว่าภายในปี พ.ศ.2568 พนักงาน 10% จะใช้ Virtual Space เป็นประจำ (กับกิจกรรมต่าง ๆ เช่น การขาย การอบรมทีมงานใหม่ หรือการสื่อสารกับทีมผ่านระยะไกล) เพิ่มขึ้นจาก 1% ในปี 2565
- ประสบการณ์แบ่งปันร่วมกัน (Shared Experiences)
ประสบการณ์แบ่งปันร่วมกันนำกลุ่มคนที่สนใจหรือมีไลฟ์สไตล์ในเรื่องเดียวกันมารวมตัวกันภายในพื้นที่เสมือน ซึ่ง Metaverse จะย้ายประสบการณ์ที่แบ่งปันร่วมกันออกจากแอปพลิเคชันเดี่ยว ๆ ที่ให้ประสบการณ์เสมือนจริง และสร้างโอกาสการพบปะ ทำงานร่วมกัน พูดคุยโต้ตอบ มีส่วนร่วม และแบ่งปันประสบการณ์ในแอปพลิเคชันที่ใช้งานร่วมกัน รวมถึงกิจกรรมสำหรับผู้บริโภค และบริการอื่น ๆ โดย Metaverse จะทำให้เกิดประสบการณ์เสมือนจริงได้แบบมีอิสระ
การ์ทเนอร์คาดการณ์ว่า ภายในปี พ.ศ. 2571 การจัดกิจกรรมสาธารณะ 10% (อาทิ การแข่งกีฬาและศิลปะการแสดงต่าง ๆ) จะเพิ่มการมีส่วนร่วมในโลก Metaverse ซึ่งเป็นการโหมให้เกิดกระแสการแบ่งปันประสบการณ์เชิงพาณิชย์ใน Metaverse เติบโตรวดเร็ว
- สินทรัพย์โทเค็น (Tokenized Assets)
สินทรัพย์โทเค็น (Tokenized Assets) นำเสนอโมเดลธุรกิจใหม่ให้กับเหล่าคอนเทนต์ครีเอเตอร์ โดยสินทรัพย์โทเค็นใน Metaverse ส่วนใหญ่จะใช้เทคโนโลยี (Non-Fungible Token Technologies หรือ NFTs) ที่ไม่สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงได้ นอกจากนี้ เทคโนโลยี NFTs ยังรองรับโมเดลเศรษฐกิจใหม่ ๆ อาทิ ให้คอนเทนต์ครีเอเตอร์สามารถเก็บรักษารายได้ส่วนใหญ่จากการขายผลงานของตนไว้ได้ตลอดไป พร้อมยังมีฟีเจอร์และฟังก์ชันทำงานใหม่ ๆ ให้ใช้งานได้ใน Metaverse ช่วยสร้างแรงบันดาลใจในวิธีการสร้างสรรค์ผลงานใหม่ ๆ ที่ไม่เพียงแต่แข่งขันกันและสร้างรายได้จากผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการเสมือนจริง แต่ยังได้รับสินค้าจริง ๆ ได้ (ในโลกความเป็นจริง)
การ์ทเนอร์คาดการณ์ว่า ภายในปี พ.ศ.2570 องค์กรธุรกิจค้าปลีกที่มีระบบอีคอมเมิร์ซ 25% จะมีการทดลองออกสินทรัพย์โทเค็นอย่างน้อยหนึ่งรายการโดยใช้เทคโนโลยี Metaverse
- การคำนวณเชิงพื้นที่ (Spatial Computing)
การคำนวณเชิงพื้นที่ผสมผสานวัตถุทางกายภาพและดิจิทัลเข้าไว้ด้วยกันเพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการใช้ชีวิตในโลกจริง และยังช่วยให้องค์กรได้รับประโยชน์จากสินทรัพย์ทางกายภาพและดิจิทัลมากขึ้น ผ่านการแสดงข้อมูลดิจิทัลที่เกี่ยวข้องและที่อาจ “มองไม่เห็น” รวมถึงเนื้อหาที่ยึดโยงผู้คน สถานที่ และสิ่งต่าง ๆ ตัวอย่างเช่น เนื้อหาดิจิทัลสามารถเพิ่มวัตถุหรือสภาพแวดล้อมทางกายภาพได้ เช่น การทำสีดิจิทัลบนรูปปั้นกรีกและโรมัน หรือเพิ่มข้อมูลของผลิตภัณฑ์หรือวัตถุเข้าไป
การ์ทเนอร์คาดการณ์ว่า ภายในปี พ.ศ.2569 แว่นตาคำนวณเชิงพื้นที่ (Spatial Computing Glasses) รุ่นที่สองและสามจะมาถึงในตลาด ก่อให้เกิดประสบการณ์ Metaverse ที่เชื่อมโยงกับโลกจริง ๆ ได้รับความนิยมมากยิ่งขึ้น