LEO Satellite Communications Services to Become Mainstream as New Business and Consumer Uses Emerge
End-user spending on low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite communications services is expected to reach $14.8 billion globally in 2026, an increase of 24.5% from 2025, according to Gartner, Inc.
“LEO satellites have primarily delivered broadband connectivity to remote locations where traditional networks don’t reach,” said Khurram Shahzad, Senior Director Analyst at Gartner. “However, new consumer and business use cases are emerging, driving communications service providers (CSPs) to expand the market. This is enabling LEO satellites to become a mainstream enterprise broadband technology.”
LEO satellites orbit closer to the Earth than traditional satellite technology, providing faster connections and lower latency. This allows them to deliver high-speed broadband and complement traditional terrestrial networks. The market is entering a rapid expansion phase, with over 20 active LEO satellite service providers and more than 40,000 satellites expected in the next few years.
“As use cases continue to grow, companies and consumers can expect consistent internet access and Internet of things (IoT) sensing anywhere, without being limited by location,” Shahzad said. “Even airplanes, ships and sea platforms will benefit from new means of network resiliency and a ubiquitous internet.”
The largest growth in LEO satellite communications services in 2026 will come from businesses and consumers in remote areas with no other connectivity options, with spending expected to increase 40.2% and 36.4% respectively. This is followed by LEO services for IoT connectivity (32%), maritime and aviation (13.8%) and network resilience improvement (7.7%) (see Table 1).
Table 1. LEO Satellite Communications Services End-User Spending Worldwide, 2025-2026 (Millions of U.S. Dollars)
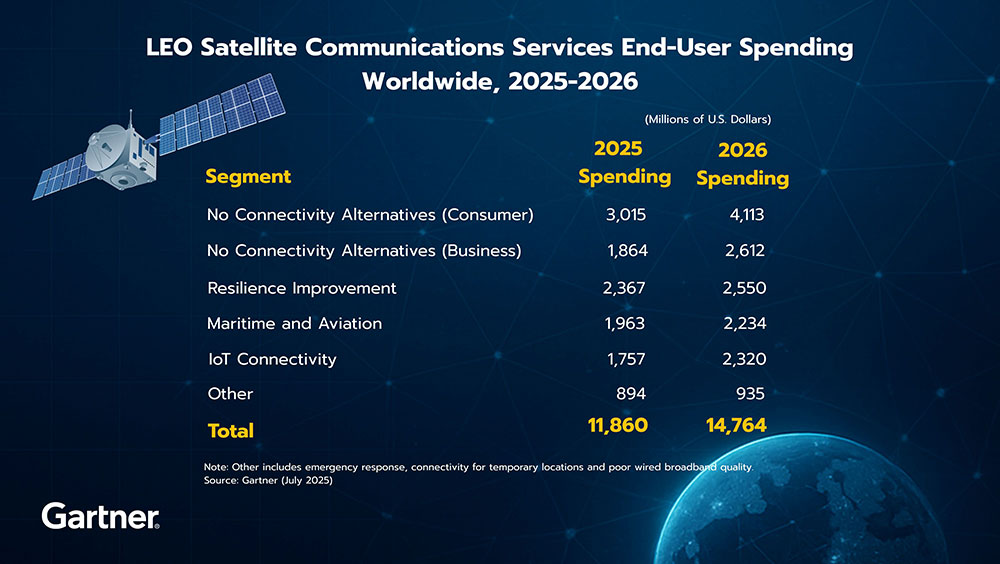 Note: Other includes emergency response, connectivity for temporary locations and poor wired broadband quality.
Note: Other includes emergency response, connectivity for temporary locations and poor wired broadband quality.
Source: Gartner (July 2025)
Emerging use cases for LEO satellite communications services can be categorized into four distinct areas:
- Fixed and Mobile Broadband Service
The main early use of LEO satellite services is for fixed and mobile broadband connectivity, especially for remote sites and to augment existing broadband connections. These services support use cases such as connectivity in areas with no broadband service, temporary locations like construction sites, or on ships and airplanes. They are also used for communication during emergency responses, or to improve resilience as fallback or backup connectivity to traditional broadband.
For example, LEO-connected drones are used in Australia to deliver 4G/5G mobile connectivity during natural disasters, while some U.S. airlines are starting to offer free high-speed Wi-Fi to passengers using LEO satellite communications services.
- Global IoT Connectivity
LEO IoT satellites complement or even replace traditional IoT networks for applications needing global coverage, with limited bandwidth and latency requirements. They can be used for global asset tracking, agriculture, oil and gas, natural resources, transportation and logistics, military sensing and security monitoring.
For example, global IoT connectivity is being deployed for land, sea and air using LEO satellites. In China, an automaker launched 20 LEO satellites to improve navigation for autonomous vehicles and plans to have a constellation of 240 satellites.
- Supplementing Mobile Broadband Services
LEO satellite communications services can supplement mobile broadband by providing seamless coverage and enhancing the user experience through direct-to-device (D2D) connections and integration with 5G non-terrestrial networks.
For example, a New Zealand CSP launched a D2D LEO satellite service that lets customers send and receive texts in the 40% of the country not covered by mobile towers. Residents in the Cook Islands have been able to use text messaging services via satellite for almost two years.
- Infrastructure Backhaul
Both CSPs and enterprises with geographically dispersed operations can leverage LEO satellites for reliable and high-bandwidth connectivity, supporting critical applications, data transfer and communication needs independent of traditional terrestrial limitations.
For example, LEO satellites can provide the necessary backhaul for the operations of government agencies and defense organizations, which often require secure and reliable communication links in remote or hostile environments.
“Despite these expanding use cases, the industry remains nascent with various limitations, including regulatory barriers in some countries and capacity constraints in certain areas,” said Shahzad. “LEO services can also encounter roaming restrictions, lack interoperability and aren’t certified for all mission-critical maritime needs. It’s important for CSPs to assess strategies on a use case basis.”
โดยบริการสื่อสารดาวเทียม LEO จะกลายเป็นเทคโนโลยีที่ได้รับความนิยม เมื่อเกิดการใช้งานในกลุ่มธุรกิจและกลุ่มผู้บริโภคเพิ่มขึ้น
การ์ทเนอร์ อิงค์ คาดการณ์ ในปี 2569 มูลค่าการใช้จ่ายของผู้ใช้ปลายทางสำหรับบริการสื่อสารดาวเทียมวงโคจรต่ำ (Low Earth Orbit หรือ LEO) ทั่วโลก จะมีมูลค่าแตะ 14.8 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐฯ เพิ่มขึ้น 24.5% จากปี 2568
Khurram Shahzad, ผู้อำนวยการอาวุโสฝ่ายนักวิเคราะห์ของการ์ทเนอร์ กล่าวว่า “ดาวเทียม LEO ส่วนใหญ่ให้บริการเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตความเร็วสูงในพื้นที่ห่างไกลที่เครือข่ายแบบเดิมไม่สามารถเข้าถึงได้ อย่างไรก็ตาม ยูสเคสการใช้งานใหม่ ๆ ในกลุ่มผู้บริโภคและกลุ่มธุรกิจเริ่มเกิดมากขึ้น ส่งผลทำให้ผู้ให้บริการสื่อสาร (CSPs) ขยายตลาดมากยิ่งขึ้น ทำให้ดาวเทียมวงโคจรต่ำกลายเป็นเทคโนโลยีอินเทอร์เน็ตความเร็วสูงหลักในระดับองค์กร“
ดาวเทียม LEO โคจรใกล้โลกมากกว่าเทคโนโลยีดาวเทียมเดิม ให้การเชื่อมต่อที่รวดเร็วกว่าและมีความหน่วงต่ำกว่า ช่วยให้สามารถส่งอินเทอร์เน็ตความเร็วสูงและเสริมเครือข่ายภาคพื้นดินแบบเดิม โดยตลาดนี้กำลังเข้าสู่ช่วงขยายตัวอย่างรวดเร็ว ด้วยผู้ให้บริการดาวเทียม LEO ที่มีอยู่มากกว่า 20 ราย และคาดว่าจะมีดาวเทียมมากกว่า 40,000 ดวง ในอีกไม่กี่ปีข้างหน้านี้
“เมื่อยูสเคสการใช้งานยังคงเติบโต บริษัทและผู้บริโภคสามารถคาดหวังการเข้าถึงอินเทอร์เน็ตที่มีความสม่ำเสมอและรับรู้ทุกสิ่งที่เชื่อมต่อผ่านเทคโนโลยีอินเทอร์เน็ตออฟติงส์ (IoT) ได้จากทุกที่ โดยไม่จำกัดสถานที่ แม้แต่เครื่องบิน เรือ และแพลตฟอร์มนอกชายฝั่ง (Sea Platform) ล้วนได้รับประโยชน์จากวิธีการใหม่ที่มีความยืดหยุ่นของเครือข่ายและอินเทอร์เน็ตที่แพร่หลาย“
ในปี 2569 การเติบโตที่ใหญ่ที่สุดของบริการสื่อสารดาวเทียม LEO จะมาจากกลุ่มธุรกิจ (Business) และกลุ่มผู้บริโภค (Consumer) ในพื้นที่ห่างไกลที่ไม่มีตัวเลือกการเชื่อมต่ออื่น โดยคาดว่ายอดการใช้จ่ายจะเพิ่มขึ้นถึง 40.2% และ 36.4% ตามลำดับ ตามด้วยบริการ LEO สำหรับการเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตออฟติงส์ (IoT) (32%) การเดินเรือและการบิน (13.8%) และการปรับปรุงความยืดหยุ่นของเครือข่าย (7.7%) (ดูตารางที่ 1)
ตารางที่ 1. มูลค่าการใช้จ่ายของผู้ใช้ปลายทางสำหรับบริการสื่อสารดาวเทียมวงโคจรต่ำ (LEO) ทั่วโลก, ปี 2568-2569 (หน่วย: ล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐฯ)
 หมายเหตุ: บริการอื่น ๆ รวมถึงการตอบสนองเหตุฉุกเฉิน การเชื่อมต่อในสถานที่ชั่วคราว และคุณภาพอินเทอร์เน็ตแบบสายที่ไม่ดี
หมายเหตุ: บริการอื่น ๆ รวมถึงการตอบสนองเหตุฉุกเฉิน การเชื่อมต่อในสถานที่ชั่วคราว และคุณภาพอินเทอร์เน็ตแบบสายที่ไม่ดี
แหล่งที่มา: การ์ทเนอร์ (กรกฎาคม 2568)
ยูสเคสการใช้งานที่เกิดขึ้นใหม่สำหรับบริการสื่อสารดาวเทียมวงโคจรต่ำ สามารถจัดหมวดหมู่ออกเป็น 4 หมวดแตกต่างกัน ดังนี้:
1. บริการอินเทอร์เน็ตความเร็วสูงแบบคงที่และเคลื่อนที่ (Fixed and Mobile Broadband Service)
การใช้งานหลัก ๆ ของบริการดาวเทียม LEO ในช่วงแรก คือ ใช้สำหรับการเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตความเร็วสูงแบบคงที่และเคลื่อนที่ โดยเฉพาะสำหรับไซต์ห่างไกล และใช้เพื่อเสริมการเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตความเร็วสูงที่มีอยู่ โดยบริการเหล่านี้รองรับยูสเคสการใช้งานต่าง ๆ เช่น การเชื่อมต่อในพื้นที่ที่ไม่มีบริการอินเทอร์เน็ตความเร็วสูง สถานที่ชั่วคราว อาทิ ไซต์ก่อสร้าง หรือบนเรือและเครื่องบิน นอกจากนี้ยังใช้เพื่อการสื่อสารในระหว่างการตอบสนองต่อเหตุฉุกเฉิน หรือเพื่อปรับปรุงความยืดหยุ่นเป็นการเชื่อมต่อสำรองหรือการแบ็คอัพอินเทอร์เน็ตความเร็วสูงแบบดั้งเดิม
ตัวอย่างเช่น โดรนที่เชื่อมต่อดาวเทียม LEO ที่ถูกใช้ในออสเตรเลียผ่านการเชื่อมต่อมือถือ 4G/5G ในระหว่างเกิดภัยพิบัติทางธรรมชาติ หรือสายการบินของสหรัฐฯ บางแห่งที่เริ่มเสนอบริการอินเทอร์เน็ต Wi-Fi ความเร็วสูงฟรีให้กับผู้โดยสารโดยใช้บริการสื่อสารดาวเทียม LEO
2. การเชื่อมต่อ IoT ทั่วโลก (Global IoT Connectivity)
ดาวเทียม LEO IoT เข้ามาเสริมหรือแม้แต่มาแทนที่เครือข่าย IoT แบบดั้งเดิม สำหรับการใช้งานแอปพลิเคชันต่าง ๆ ที่ต้องการการครอบคลุมทั่วทั้งโลก โดยใช้แบนด์วิดท์และความหน่วงที่จำกัด เทคโนโลยีดาวเทียมนี้สามารถใช้สำหรับการติดตามทรัพย์สินได้ทั่วโลก ครอบคลุมภาคเกษตรกรรม น้ำมันและก๊าซ ทรัพยากรธรรมชาติ การขนส่งและโลจิสติกส์ รวมถึงการรับรู้ทางทหาร (Military Sensing) และการตรวจสอบความปลอดภัย
ตัวอย่างเช่น การเชื่อมต่อ IoT ทั่วโลกกำลังถูกนำไปใช้สำหรับทั้งทางบก ทางทะเล และทางอากาศโดยใช้ดาวเทียม LEO อย่างเช่น ในประเทศจีนผู้ผลิตรถยนต์ได้เปิดตัวดาวเทียม LEO 20 ดวง เพื่อปรับปรุงการนำทางสำหรับยานยนต์อัตโนมัติ และวางแผนที่จะมีกลุ่มดาวเทียมถึง 240 ดวง
3. การเสริมบริการอินเทอร์เน็ตมือถือ (Supplementing Mobile Broadband Services)
บริการสื่อสารดาวเทียม LEO สามารถเสริมประสิทธิภาพอินเทอร์เน็ตมือถือ โดยให้ความครอบคลุมสัญญาณที่ไร้รอยต่อและเพิ่มประสบการณ์ผู้ใช้ผ่านการเชื่อมต่อโดยตรงกับอุปกรณ์ (Direct-to-Direct หรือ D2D) และการผสานรวมเข้ากับเครือข่าย 5G เหนือพื้นโลก (5G Non-Terrestrial Networks)
ตัวอย่างเช่น ผู้ให้บริการสื่อสารของนิวซีแลนด์ที่เปิดตัวบริการดาวเทียม D2D LEO ช่วยให้ลูกค้าสามารถส่งและรับข้อความในพื้นที่ 40% ของประเทศที่อยู่นอกเขตจากเสาส่งสัญญาณมือถือ โดยผู้อยู่อาศัยในหมู่เกาะคุก (Cook Islands) สามารถส่งข้อความผ่านดาวเทียมมาได้เกือบสองปีแล้ว
4. การเชื่อมต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานแบ็คฮอล (Infrastructure Backhaul)
ทั้งผู้ให้บริการสื่อสารและองค์กรที่มีการดำเนินงานอยู่กระจัดกระจายตามภูมิศาสตร์ สามารถใช้ประโยชน์จากดาวเทียม LEO เพื่อเชื่อมต่อกับสัญญาณที่มีความเสถียรและมีแบนด์วิดท์สูง รองรับแอปพลิเคชัน การถ่ายโอนข้อมูล และความต้องการการสื่อสารที่มีความสำคัญ โดยไม่ขึ้นอยู่กับข้อจำกัดภาคพื้นดินแบบเดิม
ตัวอย่างเช่น ดาวเทียม LEO สามารถให้การเชื่อมต่อที่จำเป็นเพื่อการดำเนินงานของหน่วยงานรัฐบาลและองค์กรป้องกันประเทศ ซึ่งมักต้องการลิงก์การสื่อสารที่มีความปลอดภัยและเสถียรในสภาพแวดล้อมที่ห่างไกลหรืออยู่ในเขตแดนข้าศึก
“แม้จะมียูสเคสใช้งานเหล่านี้ที่ขยายตัวมากขึ้น แต่ว่าอุตสาหกรรมนี้ยังคงอยู่ในช่วงเริ่มต้นและมีข้อจำกัดต่าง ๆ รวมถึงมีอุปสรรคด้านกฎระเบียบในบางประเทศ และข้อจำกัดด้านความจุเครือข่ายในพื้นที่บางแห่ง โดยบริการ LEO ยังสามารถประสบปัญหากับข้อจำกัดของการโรมมิ่ง ขาดการทำงานร่วมกัน และไม่ได้รับการรับรองสำหรับความต้องการทางทะเลที่สำคัญต่อภารกิจทั้งหมด จึงเป็นเหตุผลสำคัญที่ผู้ให้บริการสื่อสารต้องประเมินกลยุทธ์บนพื้นฐานของยูสเคสที่จำเป็นในการใช้งาน” Shahzad กล่าวเพิ่มเติม
 หมายเหตุ: บริการอื่น ๆ รวมถึงการตอบสนองเหตุฉุกเฉิน การเชื่อมต่อในสถานที่ชั่วคราว และคุณภาพอินเทอร์เน็ตแบบสายที่
หมายเหตุ: บริการอื่น ๆ รวมถึงการตอบสนองเหตุฉุกเฉิน การเชื่อมต่อในสถานที่ชั่วคราว และคุณภาพอินเทอร์เน็ตแบบสายที่